탐방
First Step to Commercialize Organoid: Organoid Science’s Vision
by Joungmin Cho
Establishing an organoid-based new drug development platform and developing an organoid regenerative medicine

▲CEO of Organoid Science.
Organoid Science was established in October 2018. It aims to develop therapies for incurable diseases using organoid grown in vitro from stem cells in three dimensions to mimic human organs.
Interviewed by Bio Spectator, Organoid Science CEO Yoo Jong-man has recently said: “We have studied organoid as part of our stem cell research. During the research, we have found that organoid is extremely valuable. Thus, we decided to bring organoid technology to life beyond the lab and develop it further by running a business.”
Organoid Science will build a platform for new medicine development using organoids which highly mimic human organs and develop regenerative medicines based on expansion and regenerative capacity of adult stem cells. Yoo said, “We’d like to become a leader to commercialize organoid technology which is very new in the domestic market.”
◇Organoids highly mimick human organs beyond two-dimensional cell culture. They can be customized for each patient, enabling swift decision making during new drug development
“Under the current technology, organoids derived from stem cells can be grown in vitro in three dimensions. They can mimic intestines, stomach tract, liver, and complex organs such as the brain. They are also very similar to human organs. Thus, they are highly useful as a prototype platform to examine toxicity and efficacy since they reflect each patient’s characteristics,” Yoo explained. “An accurate and fast decision making about a candidate material is essential in the process of drug development which requires a lot of money. Organoids can accelerate the process by offering necessary data for swift decision-making.”
Organoid Science is particularly focused on tumor organoids appropriate for anti-cancer drug development. Tumor organoids produced from patient tumor tissues can be used to analyze custom anti-cancer drugs and predict their medicinal efficacy for each patient. “Our tumor organoid model not only uses tumor cells, but also grows cells in vitro which make up the tumor microenvironment. Therefore, the tumor microenvironment can be reflected. This is why our model is special,” a company official said.

A tumor once formed is surrounded by various cells such as a blood vessel, immune cell, fibroblast, inflammatory cell, and lymphocyte. This is called the tumor microenvironment. Tumor cells and the microenvironment affect each other while multiple factors in the environment play a role in tumor heterogeneity. Tumor microenvironment has been recognized for its importance in recent years in relation to an anti-cancer drug efficacy and reaction. Thus, experiments reflecting the tumor environment are more and more required.
Organoid Science has developed a platform technology in which a tumor environment is established outside the human body. By screening the environment, an innovative anti-cancer drug can be developed. Mr. Yoo said, “We can provide more accurate and trusted screening data reflecting the body environment more realistically than organoids with cancer cells only.” In an experiment performed by Organoid Science to see if its platform shows consistency with drug reaction in reality using stem cells extracted from the pancreas, an organoid was manufactured and drug screening was implemented. As a result, a speedy screening was possible within three weeks and success rate was more than 80%.
Organoid Science is further planning to work with pharmaceutical firms and research centers for joint development, ultimately building its own pipeline beyond the current simple screening and analysis service based on its platform technology. “Now we are developing a new organoid drug platform for pancreas, lung, and colon cancers through joint effort with chemical researchers and CHA Medical Center,” Yoo added.
◇Developing a regenerative medicine based on adult stem cells to address complications after radioactive treatment
Organoid Science has started to develop regenerative medicines based on an idea that organoids are optimized to grow adult stem cells in vitro. “The organoid technology is perfect to culture adult stem cells which make up human body tissues,” the CEO described.
Organoid Science is developing medicines designed to induce regeneration by growing target adult stem cells in vitro in the form of organoid and inserting them into dysfunctional organs. Organoid Science is equipped with a safe and cost-efficient organoid technology to provide collagen-based growth support in vitro instead of matrigel which is hard to apply to the human body. It has also discovered alternative compounds to existing animal-derived components. “We have been able to save production costs up to 20% compared to the past by replacing growth factors with small molecule compounds,” Yoo added.
Organoid Science has also developed a culture medium for organoid mass production where reinforced compounds are adopted to prevent division or slower performance of adult stem cells during growth in vitro which is considered one of the obstacles for mass production. In addition, along with experts, Organoid Science has advanced an optimal technology and established a protocol for freezing/defrosting organoids to improve the yield of freezing/defrosting.
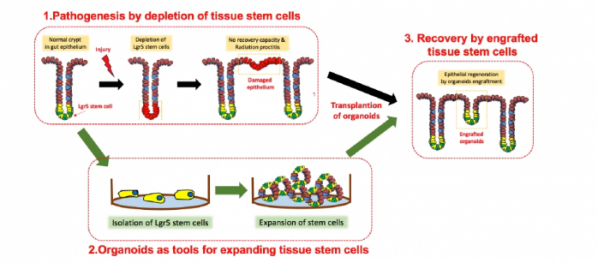
Organoid Science is about to round off the lab-based GMP production process development. It is further planning to evolve a commercial GMP process in large scale from next year. During the development of regenerative medicine, adverse effects appearing after radioactive treatment will become the first target to be addressed to make medicines for salivary gland dysfunction and radiation proctitis.
“We are determined to actively introduce good candidate technologies from outside based on established platform for regenerative medicines,” CEO Yoo said. “Of course, we know that we face a lot of challenges ahead as the idea of organoid regenerative medicine is very new in the market. However, given such a remarkable treatment effect, we can be highly competitive.”
“It has not been long since the development of organoids worldwide. Organoid Science is committed to developing effective treatments in the clinical field and playing a leading role in organoid commercialization,” he added.














![[BioS 레터]무균주사제 공급망 변화와 CDMO 대응](https://img.etoday.co.kr/crop/77/77/2262816.jpg)




