탐방
LegoChem, expanding businesses 'ADC Platform→enter US clinical trials'
바이오스펙테이터 Sungmin Kim 기자
LegoChem Biosciences vowed to lead the project for non-clinical safety evaluation of ADC to target solid cancer. The meaning of Takeda deal and three strategies of the next-generation ADC development?
Last year, the antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) field ushered in a turning point. The milestone event was that Astrazenesca signed a 1.35 million deal to purchase rights for development and commercialization in certain regions of HER2 ADC ‘DS-8201(product name: Enhertu)' developed by Daiichi Sankyo, the forerunner in the ADC field. This was the biggest contract as a single new drug among license contracts for the past 10 years.
Among domestic biotech companies, LegoChem Biosciences stood out. Last March, LegoChem Biosciences concluded a deal worth up to $400 million for technology transfer of the next generation ADC linker technology to Takeda. This technology requires a high concentration of resources to the extent that more than half of LegoChem Biosciences' current total manpower were input in ADCs. LegoChem Biosciences is establishing its foothold as a next-generation ADC linker platform developer in the global market.
Apart from that, the company is expected to undergo new changes from this year. CEO Kim Yong-Ju wants to raise the company's profile as a platform developer one notch up by adopting 'Gilead model,' which he has emphasized since the founding of the company. CEO Kim announced this plan on January 8, 2020 at 'Daejeon Promising Bio-Startup Company IR conference (First Half of Year 2020).' Let's get into more details.
“I had a big worry last year. I thought that platform technology would continue to be a pillar of our business, but I was worried about how I could make use of ADC new drug candidates that had been developed so far. Many will not agree on an idea that a research-oriented biotech company enters the clinical trial market from the very beginning. Gilead sold many new drug candidates in the early stage and accumulated skills before conducting clinical trial development by itself. After having deep thought, we decide to carry out clinical development of three ADC new drugs which are currently in non-clinical stage.
LegoChem Biosciences enters the full-fledged development mode of ADC new drugs. It plans to set up a subsidiary in Boston, the US and to build a clinical development center as well as an innovation center. LegoChem Biosciences plans for clinical development of three ADC new drug programs within this or next year. Three programs will be performed simultaneously as non-clinical trials: ▲ LCB71: ROR1 ADC joint developed with ABL Bio, ▲ LCB73: CD19 ADC joint developed with Novimmune, a Swiss biotech company, ▲ LCB67: DLK1 ADC by introducing antibody from Y-Biologics.
Ahead of an important milestone, the results of phase 1 clinical trial of HER2 ADC ‘LCB14’ on which LegoChem Biosciences transferred technology to Fosun Pharma of China are expected to come out soon. LegoChem Biosciences targets IHC1+ or IHC2+ patients with a low HER2 expression to HER2+ metastatic breast cancer in the long run.
LegoChem's ADC technology: Linker and PDB prodrug
LegoChem Biosciences started the technology development of the next-generation ADC linker in the early 2010s. The followings were verified based on ConjuAll platform: ▲ a constant drug-antibody ratio (DAR) as a single substance, ▲ excellent pharmacological (PK) properties similar to those of monoclonal antibodies, ▲ excellent blood stability, ▲ beta-glucuronidase(an enzyme with ahigh expression in cancer cells)-mediated drug release.
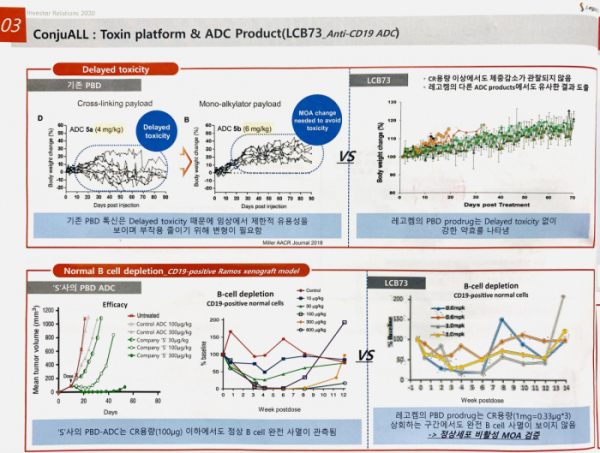
Another technology that LegoChem Biosciences emphasizes is new PBD (Pyrrolobenzodiazepine), a toxic anti-cancer drug. PBD has the greatest potency among various toxic anti-caner drugs combined with ADC. However, there are some skeptical opinions about its side effects found in clinical trial. In the clinical trial, delayed toxicity was observed. LegoChem Biosciences proposed an idea to overcome such limitation. It is called 'PBD Prodrug concept,' in which it remains inactivated to normal cells but activated to a specific enzyme in cancer cells. It has two advantages. First, it has safe application to solid cancer. LegoChem Biosciences confirmed the drug efficacy and safety by administering PBD prodrug to CD19 antibody in an animal experiment. Second, PBD prodrug is made of homogeneous composites by improving the bad properties of the existing PBD drugs.
Meaning of Takeda Deal & LegoChem's three strategies for next-generation ADC development?
Attention should be paid to the potential of ADC platform. Previously, the concept of ADC was to deliver toxic anticancer drugs specifically to cancer tissues. However, thanks to recent advances in linker technology, the concept is now expanding. We need to take a look at Takeda deal from this perspective.
CEO Kim said, "It took three years and half to conclude Takeda deal. There is a reason for this. A common ADC that binds toxin anti-caner drug to antibody generally takes one or two years. However, it took a long time because it attached small molecule to immuno-oncology (IO) instead of binding toxin." This immunology's concept to target molecule is to drop small molecules into tumor microenvironment (TME). In reality, immune anticancer drugs actually have many problems to overcome. For example, there are side effects including cytokine release syndrome.
LegoChem Biosciences comes up with three strategies to develop next-generation ADC with its own capacity. First, it is a concomitant administration strategy. LegoChem Biosciences discovered a combination drug that could generate synergy effect with ADC three years ago and have found three kinds of small molecule immunology candidate substances. In future, the company will develop new ADC and its combination therapy with immunology. Second, it is the double antibody ADC (BsAb ADC). Third, it is to expand indications to other diseases. LegoChem Biosciences is expected to be able to expand its technology domain from immunology ADCs to antifibrotic ADCs and antibiotics ADCs.
CEO Kim added, "In future, ADC platform is going to expand to chronic diseases. It is about attaching small molecule to antibody and delivering it to the target site. For this, the company is developing more sophisticated linkers by itself. We try to make the best of the advantage of linkers and payload.
Launch back-up 'autotaxin inhibitor series'
Last year, the company underwent an important event. LegoChem Biosciences concluded a deal with Boehringer Ingelheim on ‘BBT-877,’ an autotaxin (ATX) inhibiter developed as a IPF candidate substance licensed out from Bridge Biotherapeutics in 2017, and the deal is expected to generate 45 million euros as down payment and short-term milestones and up to 1.1 billion euros as drug development, regulatory, and sales milestones. Under the terms of the contract, LegoChem Biosciences will receive 45% of revenues from Bridge Biotherapeutics.
The autotaxin inhibitor has greater potentials. The starting point of BBT-877 was an anticancer drug project. CEO Kim said, "If we look at the working mechanism of autotaxin, it is a target exactly related to cell migration. It is an important target for cancer metastasis and shows expression not to all types of cancers but to specific cancers. By inhibiting this signaling, it can change fibrosis cycle." Also, it is noteworthy that inflammatory reaction and fibrosis occur together in tumor tissues. Based on this mechanism, BBT-877 can be applied to fibrotic diseases and ultimately to cancer diseases.
LegoChem Biosciences also has backup plans for new drug candidate substances after BBT-877. According to the contract, it can develop its proprietary autotaxin inhibitor. CEO Kim said, "There is no other company that has more experiences of new drug development in autotaxin target than my company. The backup program in autotaxin inhibitor is to target nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and dementia. In addition, another possibility is the concomitant administration with ADC. When ADC new drug is concomitantly administered with autotaxin inhibitor in malignant solid carcinoma models, including liver cancer, pancreatic cancer, and ovarian cancer." BBT-877 cannot penetrate blood-brain barrier.













![[인사]종근당 계열사, 2026년 임원승진 인사](https://img.etoday.co.kr/crop/77/77/2277741.jpg)



