탐방
IMBiologics unveils next-generation IgM platform aiming new concept of immune cell engager
by Sungmin Kim
Development strategy and positioning of ‘OX40LxTNF-α bispecific antibody.’..What are the 5 differentiating points of the ‘IgM platform’ and it's applications in anti-cancer?

▲GyongSik Ha, CEO of IMBiologics
IMBiologics is seeking a change different from the past as it unveils an IgM-based antibody platform after two years of establishment. Most antibody platforms are based on IgG, and even in the global market, platform development using IgM antibodies is not common. An IgG antibody has two antigen-binding sites, whereas an IgM antibody has about 10 ~ 12. Globally, only IGM Biosciences, which entered a partnership deal with Sanofi in March this year, is known as a company with an IgM antibody platform.
In the midst of this, in April of this year, IMBiologics completed a patent application for 'ePENDY' technology, a long-acting multivalent antibody platform that overcomes the limitations of existing IgM antibodies in terms of new drug development, and appeared in the industry. It is throwing a fresh keyword of the next-generation IgM multi-antibody platform to the domestic industry.
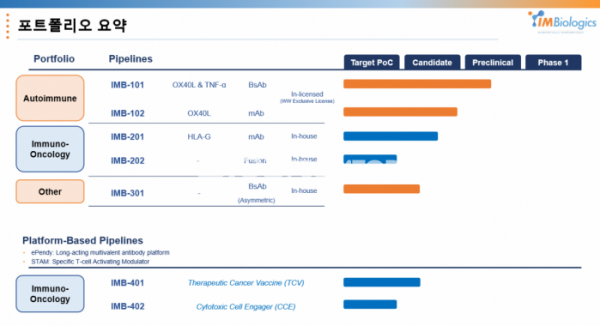
Until now, IMBiologics has been known only as a company established when HK inno.N (formerly CJ Healthcare) introduced the OX40LxTNF-α bispecific antibody ‘IMB-101’, which is an autoimmune disease target. But now, it is showing an upgraded aspect. IMBiologics is a company that researchers, who have been leading the preclinical development process from the idea of autoimmune disease bispecific antibody asset since the old CJ Healthcare days, started with a willingness to continue clinical development.
IMBiologics was established in August 2020 and started in earnest three months later when it licensed the global development and exclusive license of IMB-101 from HK inno.N. It is an independent form without capital participation of HK inno.N.
GyongSik Ha, CEO of IMBiologics, said, "At the time of establishment, we thought that one asset alone would not have the possibility of sustainable growth of the company, so we needed an asset that we develop ourselves. We needed to study the platform related to antibodies, and we thought it would be advantageous to build a platform with IgM antibodies while thinking about vaccines." "We have implemented a platform that has been only an idea for the past two years and have finally completed a patent application for ePENDY technology this year."
The clinical start of IMB-101, the lead program next year, is also expected. After introducing the OX40LxTNF-α bispecific antibody ‘IMB-101’, IMBiologics is finishing the study (IND-enabling study) for the submission of the clinical trial protocol. In the first half of next year, IMB-101 is planned to be submitted an IND to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). As the platform and tasks have been sophisticated, the R&D manpower of the company, which was established with five researchers from CJ Healthcare, increased to 23.
The headquarters and research center of IMBiologics is located in Gwanggyo, Gyeonggi-do, and since its establishment, it has secured a total investment of 17 billion won, including seed investment (4 billion won) and Series A (13 billion won). The lead program, IMB-101 dual antibody, was selected as a project for the Korea Drug Development Fund (KDDF) in March this year and will receive a total project cost of KRW 2 billion (KRW 1.5 billion from the project group) until approval for phase 1 clinical trials.
What is the positioning of the OX40LxTNF-α bispecific antibody strategy?
OX40 is a co-stimulatory immune checkpoint molecule that activates immunity as one of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor family. During the boom in immuno-oncology, OX40/OX40L signaling was developed focusing on immune activation factors, but no clear efficacy results were obtained. Rather, drugs that inhibit it are a target that has recently been highlighted as it has produced positive results in autoimmune diseases.
Large deals followed in the last year alone. In January last year, Sanofi acquired Kymab for $1.45 billion, including upfront fee of $1.1 billion, to secure 'KY1005 (SAR445229)', an OX40 ligand (OX40L) antibody which is developed as an autoimmune disease treatment under a phase 2 clinical stage. In June, Amgen also followed Sanofi and entered the OX40/OX40L competition. Amgen purchased the OX40 antibody 'Rocatinlimab (KHK4080)' from its long-time partner, Japan's Kyowa Kirin, for a total of $1.25 billion, including upfront fee of $400 million, and is leading the way in phase 3 clinical trials. The remaining clinical development asset is Ichnos Sciences' OX40 antibody 'Telazorlimab (ISB 830; GBR 830)' of the US.
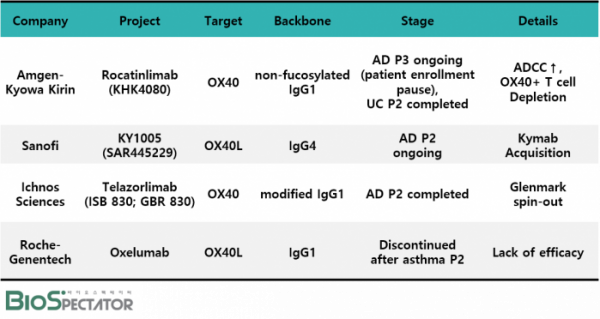
▲OX40 clinical asset development status, Source: BioSpectator
Meanwhile, IMBiologics is positioning it as a drug targeting rheumatoid arthritis (RA), based on the unique mechanism of the OX40LxTNF-α bispecific antibody.
First of all, the IMB-101 task began by looking at the possibility of OX40L as a treatment target in autoimmune diseases. It has seen the possibilities in three main aspects. First, OX40/OX40L signal transmission may activate immunity in various aspects. Specifically, OX40 is not expressed in naive T-cells, but is a factor that stimulates them by expressing them as they are activated. At the same time, OX40L is expressed in antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as B cells and dendritic cells (DCs) to stimulate them.
Second, OX40L expressed by APC plays a role in balancing T cells and regulatory T cells (Treg). At that moment, unlike T cells, OX40L plays a role in inhibiting the activity of Treg, which inhibits excessive immunity in autoimmune diseases. It is observed that Treg has decreased in the lesions of patients with autoimmune diseases. Third, recent studies have shown that OX40L signaling activation is involved in autoantibody production.
In addition, OX40/OX40L signaling overexpression is observed in several autoimmune diseases, and expression increases with disease progression in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic erythematous loops (SLE).
On top of that, IMBiologics chose a strategy that inhibits OX40L while also inhibiting TNF-α at the same time. OX40/OX40L signaling is known to have a comprehensive effect on Th1, Th2, and Th17 in autoimmune diseases, and TNF-α is selected to enhance signal targets that can enhance Th1 and Th17 inhibitory efficacy.
CEO Ha said, "Allergy diseases such as asthma and atopic dermatitis are mainly related to Th2, and based on the clinical results of oxelumab from asthma patient population, OX40/OX40L target was judged to be more suitable for autoimmune diseases involving Th1 or Th17. By adding TNF-α inhibitory ability, IMB-101 has set its target indication as rheumatoid arthritis, a typical Th1-related disease, and plans to expand its indications in the future.”
Another advantage is expected. While inhibiting TNF-α, an innate inflammatory cytokine that has been proven effective in rheumatoid arthritis patients, it can regulate the overall immune response while inhibiting OX40L, which is important for the adaptive immune response. CEO Ha said, “Currently, most drugs targeting rheumatoid arthritis are focused on controlling specific cytokines, but there are 12 types of immune cells and 30 types of cytokines involved in autoimmune diseases.” “If both factors are targeted simultaneously using a bispecific antibody, the efficacy can be improved, and we expect that the impaired immune balance will be restored in the long term,” he added.
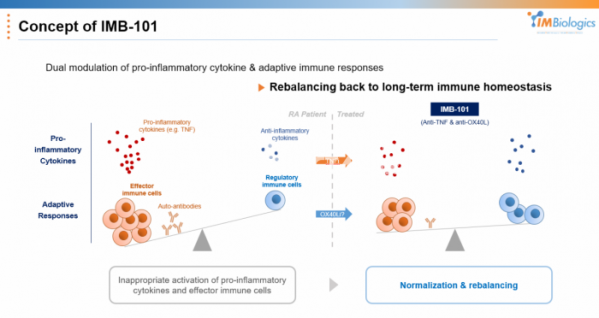
IMB-101 is a '2+2' form in which two TNF-α inhibitory scFvs are bound to an antibody that inhibits OX40L. Each signal transduction is inhibited, and there is no antibody-dependent cytotoxicity (ADCC) function using an IgG4 antibody. The TNF-α binding site exhibits a similar level of inhibitory activity to that of Humira. When designing various types of bispecific antibodies, the most suitable form was determined in consideration of the inhibitory ability, physical properties, and half-life of each target.
Differentiation is expected regarding the mechanism and efficacy of the OX40L inhibitory site. IMB-101 has a different mechanism of inhibiting OX40L compared to Kymab's KY1005. According to epitope mapping, IMB-101 inhibits the OX40/OX40L interaction, whereas KY1005 acts in a manner that prevents the formation of OX40L trimer. In addition, in the in vitro assay, IMB-101 had higher efficacy in inhibiting solubility and inhibiting its membrane OX40L compared to KY1005.
In terms of safety, it is judged that there is an advantage over OX40 drug. CEO Ha said, “We judged that OX40 inhibitors inhibit T cells, which may cause long-term safety issues, so inhibiting OX40L seemed advantageous. On the other hand, OX40 manifests itself in both blood and tissues, affecting systemic immune control. At the same time, OX40L has the advantage of being able to specifically target lesions as it is mainly expressed high in inflammatory tissues.”
The rheumatoid arthritis treatment market targeted by IMBiologics uses chemically synthesized antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) such as methotrexate (MTX) as the first treatment, and then prescribes biological antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) from the second treatment. At this time, the biopharmaceutical market is formed around TNF-α drugs such as Humira, and after that, other TNF-α drugs are prescribed to patients who do not comply. Recently, oral JAK inhibitors have been released as a target specific treatment (tsDMARDs) option, but side effects such as cardiovascular (CV) and carcinogenesis continue to be an issue.
Still, the unmet needs of the rheumatoid arthritis treatment market lack effective treatment options for patients who fail or refuse to comply with TNF-α treatment. In patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis, the response rate is limited and the response period is short such as two years. It is also a market where IMBiologics is looking for opportunities.
When the research team first conducted a conceptual proof (PoC) experiment on a new mechanism of action, IMB-101 showed additional inhibitory effects compared to TNF-α or OX40L monoclonal antibodies in animal models.
Next, the advantage was confirmed by targeting TNF-α and OX40L together in the rheumatoid arthritis model. In an in-vitro setting, IMB-101 effectively regulated several cytokines, including IL-2, IL-17 and IL-21 compared to monoclonal antibodies. In addition, ex-vivo experiments confirmed the equivalent or improved efficacy of Humira in synovial fluid mononuclear cells (SFMC), an immune cell extracted from the lesions of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. In particular, while the inflammatory signal worsened in the case of patients who did not respond to drugs during treatment with Humira, no such paradoxical effect was observed when IMB-101 was administered. This is why it is expected to be effective in TNF-α refractory patients.
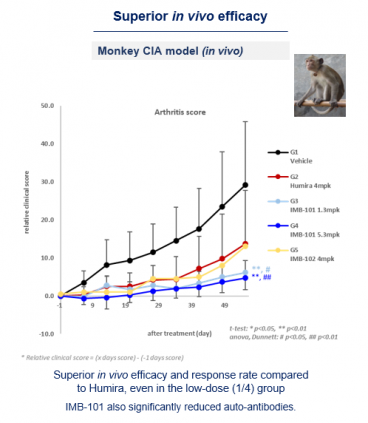
Key data is effective in the monkey rheumatoid arthritis model. IMB-101 showed a higher response rate than Humira at a quarter concentration of Humira, and also significantly lowered autoantibody levels. CEO Ha said, "Mouse has a low homology of OX40 and OX40L with humans, and there is a limitation in that data reproducibility is poor even if a humanized model is used. Therefore, we have been conducting experiments on monkey models since last year, and we have obtained encouraging efficacy data.”
Furthermore, it also confirmed the effect of reducing bone damage. When the degree of bone damage was measured as an inflammatory response in the monkey rheumatoid arthritis model (by X-ray imaging), at a certain dose or more of IMB-101, it was confirmed that bone damage was reduced compared to Humira. In addition, as a result of the mechanism study, IMB-101 had a high efficacy in inhibiting osteoclastogenesis compared to Humira.
IMBiologics confirmed that, in monkeys, IMB-101 had a pharmacokinetic (PK) profile similar to that of the existing antibody, and showed similar bioavailability (BA, 96.3%) to that of intravenous (IV) even with subcutaneous (SC) administration. It also confirmed the possibility of development as an SC formulation. IMBiologics is currently conducting a GLP toxicity test, and plans to submit an IND for phase 1 clinical trials in the US in the first half of next year.
Next-generation IgM platform concept, 'versatility' as an immuno-oncology drug
Another axis that will lead IMBiologics in the future is the IgM-based multi-combination platform 'ePENDY'. IgM (immunoglobulin M) is the first type of antibody secreted when external infectious bacteria enter the innate immunity because it can recognize the glycolysis pattern. It has a multi-coupler structure and has 10 pentamers including J-chain or 12 hexamers without J-chain. The IgM has a lower affinity to an antigen than the IgG having two binding groups, and has a high total avidity because it has 10 or 12 arms. The resulting molecular weight ranges from 900 to 1050 kDa.
IgM is structurally easy to induce clusters of target antigens, and is known to have complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) activity by binding to C1q to form clusters. In addition, IgM antibodies are known to bind to receptors such as pIgR, Fcα/μR, and FcμR.
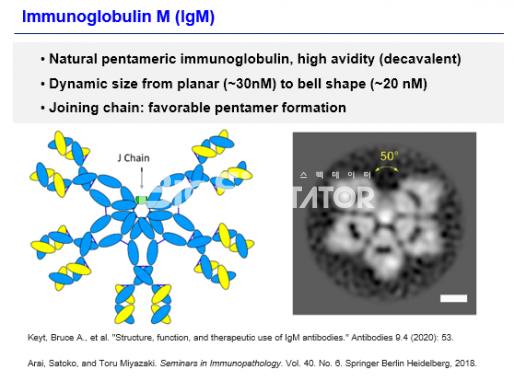
CEO Ha said, "The final target is a therapeutic vaccine for an anti-cancer treatment. As TCR forms a cluster, peptide is recognized through MHC and cytokines are secreted. In this process, we noted that TCR or immunomodulatory targets have many characteristics of clusters. I thought it would be advantageous to have a lot of binding couplers in terms of avidity, so I focused on the characteristics of IgM antibodies." He said, "We expect it to have strong effects even at low drug concentrations."
However, attempts to develop new drugs using IgM antibodies have been slow. Clinical trials have been conducted based on the fact that IgM antibodies can recognize lipopolysaccharides, glycoproteins, and glycans. Safety was confirmed in clinical trials, but there were no clear results. Then, as IGM Biosciences, which was established in 2010, recently promoted clinical development of CD3 target T cell engager applied with IgM, the concept of IgM antibody-based platform began to draw attention in the global industry.
IGM's new approach to IgM antibody platform also led to a agonist agent drug discovery deal with Sanofi in March this year targeting autoimmune, inflammatory and cancer diseases. However, the lead program CD20xCD3 "IGM-2323 (10+1 structure)" had lower-than-expected efficacy in phase 1 clinical trials for lymphoma, and there are still areas to be studied, such as the strongest drug response rate (ORR 60%) in the lowest dose (100mg).
IMBiologics decided that IgM had to overcome its existing shortcomings in order to be applied to the development of new drugs and developed the next-generation IgM platform "ePENDY" technology that overcame these limitations. There are mainly five limitations of IgM analyzed by the company, and each is implemented to supplement.
First, a hinge was introduced to increase biological activity/binding affinity. CEO Ha said, "IgG has the advantage of high flexibility because it has a hinge in structure," adding, "IgM is known that the CH2 domain acts as a hinge, but it is unclear whether it can actually act as a hinge." "It is known that there are only a few binding sites that can be bound in the body due to structural steric hindrance," he explained. With the introduction of hinges, ePENDY's avidity has increased several tens of times compared to existing IgM.
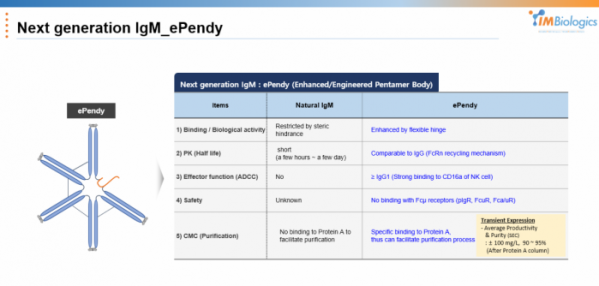
Second, its half-life is increased. In literature, the half-life of IgM is 5 days, but in practice it is less than 1 day. IMBiologics introduced an FcRn binding group to increase the half-life to a level similar to that of an IgG antibody. Third, ADCC activity was introduced. IgM does not have ADCC activity, but IMBiologics introduced a CD16a binding site capable of activating NK cells. Accordingly, in an in vitro assay, it was confirmed that ePENDY has tens to thousands of times ADCC activity than IgG. Fourth, in consideration of safety, affinity to FcμR was eliminated. CEO Ha said, “Since no drug has been marketed as an IgM antibody, drug safety cannot be predicted. Therefore, we engineered it to have properties similar to those of an IgG antibody.”
Finally, it improved the yield of production. "The biggest issue in terms of IgM CMC is that it is difficult to purify because there is no part that binds to protein A," CEO Ha said. "We expect high productivity by adding protein A binding part to ePENDY to facilitate the purification process."
What is expected in the future is the versatility of the ePENDY platform. IMBiologics expects to be able to apply ▲ antibody (scFv, Fab) ▲ protein ligand (soluble ligand, extracellular membrane domain) ▲ HLA (human leukocyte antigen) to the ePENDY platform built in this way.
IMBiologics focuses on two major directions in the field of immuno-oncology drugs. First is a therapeutic cancer vaccine platform, “STAM.ePENDY (or STAM.eP; specific T cell activating modulator)" in the form of HLA-A/peptide loaded with a peptide targeting cancer cells in HLA-A interacting with T-cell receptor (TCR).
Based on HLA, it has the advantage of minimizing toxic side effects by activating cancer cell-specific CD8+ T cells and targeting internal proteins in cancer cells through HLA. In addition, it is possible to bind co-stimulating factors such as CD28. In conclusion, the concept is to replace the role of dendritic cells (DCs) used in the development of anticancer vaccines. In a study conducted with "IMB-401 (undisclosed)" applying STAM.ep, CD8+ T cells for cancer antigens were activated, and conceptual verification data were secured.
In another direction, it is researching an engager platform that can activate both NK cells and T cells, and there is an IMB-402 (undisclosed) project to which it is applied. As a part that attracts T cells to the ePENDY platform, it is a ‘1+10’ type T cell engager in which one domain that specifically attracts CD8+ T cells and 10 domains that target cancer cells are hung. In addition, it is possible to activate NK cells through the ADCC action of the antibody. It is expected to mainly target naive T cells that have not yet encountered cancer cells.
HLA-G immuno-oncology and anemia disease
IMBiologics does not limit the project to autoimmune diseases or platforms. While developing the IMB-101 project and ePENDY platform, the monoclonal antibody immuno-oncology drug and agonist antibody ‘IMB-301 (undisclosed)’ project targeting anemia diseases are also underway.
The target that IMBiologics is paying attention to in the field of immuno-oncology is the HLA protein. Proteins in HLA belong to MHC class I, and are broadly divided into two categories. First, there are HLA-A, B, and C belonging to HLA class Ia, of which polymorphism is large. These proteins induce antigen-specific T cell activation by interacting with the TCR. The others are HLA-E, F, G, and H belonging to HLA class Ib that have the opposite action. It is relatively low on polymorphism and interacts with immunosuppressive receptors to induce an immune avoidance mechanism.
IMBiologics is working on a project for HLA-G antibody ‘IMB-201’ and Trap fusion protein ‘IMB-202 (undisclosed)’ with different characteristics.
HLA-G is known as an immune tolerance molecule that prevents the fetus from being attacked by maternal immunity, and it has recently been found that HLA-G expressed in cancer cells interacts with ILT2 expressed by immune cells to induce an immune avoidance mechanism. Accordingly, IMBiologics has a concept of increasing immune activity by inhibiting HLA-G with antibodies.
IMB-201 is on an antibody optimization step, and research is also underway to apply it to the ePENDY platform. CEO Ha said, "The most important thing in drug development targeting HLA proteins is selectivity. These proteins have the complete opposite effect of immune activation or inhibition depending on the class. In particular, HLA-A, B, and C play a key role in innate and adaptive immunity, and drug development is difficult due to their high polymorphism. We found drug candidates that have high specificity for HLA-G and do not bind to HLA-A, B, and C."
The related deal is also active. Gilead Sciences acquired ‘TTX-080’, an HLA-G antibody, from Tizona Therapeutics in 2020, which is about to undergo a phase 1 clinical trial. Also last year, Sanofi acquired the ILT-2 antibody ‘BND-22’ from Biond Biologics, which is preparing for a phase 1 clinical trial.
Leadership
When CEO Ha founded IMBiologics, he had the will to start the bispecific antibody project and lead it to the end of clinical development.
CEO Ha previously gained experience in clinical teams and marketing PMs for anticancer drugs at CJ healthcare, and as CJ closed its bio business, he conducted business development and research at antibody biotech. Then, in 2011, CJ began researching proteins, antibodies, and biosimilars again and he joined. Since then, he has been a senior researcher at CJ CheilJedang and head of the BIO Research Center at HK inno.N.
After that, HK inno.N (formerly CJ Healthcare), which was acquired by Kolmar Korea in 2018 and after discussion with the company, IMBiologics was established by licensing in the IMB-101 project. At that time, Dr. Chungmin Lee, who was in charge of the new biopharmaceutical group including this project, served as the CTO of the IMBiologics Research Center, and 4 researchers including Dr. Hong Jai Lee, who conducted the platform research, also joined. Dr. Chihye Park, who previously served as the head of the clinical medicine center at HK inno.N, also joined last year as the head of the clinical development division (CDO).
In addition, Dr. Insoo Jung, who was in charge of national project planning/technical evaluation in the Korea Institute of Industrial Technology Evaluation and Planning previously, is the chief business development and COO of the company, and Eunsung Kang, who has 18 years of CMC research experience at Dong-A ST, joined as the chief of CMC Center.
The company's motto, which CEO Ha thinks, is a " excellent performance company” centered on working-level staff with development capabilities in the industry. The development timeline established at the beginning of its establishment is also going as planned. "We are setting feasible goals when starting a company and positioning it as a company that keeps its promises," he said. "I think Biotech's way is to set clear goals to go, execute invested funds, and maintain a cycle of data." "We will also maximize shareholder value through L/O," he said.

▲Leadership of IMBiologics














![[인사]프로티움사이언스 실장·팀장급 인사](https://img.etoday.co.kr/crop/77/77/1860144.jpg)




