기업
AprilBio, 'SAFA Platform' Bind to Albumin.."Entering Clinical Trials This Year"
by Yoonseok Suh
Development of Long-Acting Drugs based on Two Core Technologies, such as Human Antibody Library 'HuDVFab' and 'SAFA'.."Lead Pipeline, CD40L Antibody 'APB-A1', Entered Phase 1 This Year"

Sang-hoon Cha, CEO of AprilBio, said “We will develop long-acting drugs with an extended half-life than conventional drugs using our own antibody library and SAFA(Anti Serum Albumin Fab Associated) technology, a long-acting drug development platform,” and "In particular, a drug-using SAFA technology is expected to remain for 20 to 25 days in the body, so it will be possible to develop a long-acting drug that is administered once every 2 to 4 weeks".
The company's proprietary technology SAFA, a long-acting antibody-drug platform, utilizes human Fab antibody fragments that bind specifically to serum albumin to deliver extended half-life.
Technology for long-acting can be divided into two types: △ increasing the size of the protein to lower the kidney filtering efficiency △ increasing the residence time in the bloodstream. AprilBio's technology is a concept that prolongs the residence time in the body, and similar methods include Genexine's hybrid Fc fusion protein platform technology and Hanmi Pharmaceutical's Labscovery technology. In addition, AprilBio owns the human antibody library 'HuDVFab'.
Founded in 2013 by CEO Cha, AprilBio is a company that has long been unknown. AprilBio received a seed investment from SM Sino Technology Investment in 2016 and began to attract attention last year when Yuhan Corporation participated in Series B investment. Since then, in March of this year, Yuhan Corporation invested 10 billion won additionally through capital increase with third-party allocation to acquired a 13.76% stake of April Bio and registered as the 2nd largest shareholder.
In the United States, April Bio is expected to start phase 1 clinical trial of 'APB-A1', a candidate substance for autoimmune disease drug, which is the lead pipeline this year. Meanwhile, April Bio is preparing for a special listing on the KOSDAQ market this year through technology evaluation. BioSpectator looked into AprilBio's platform technology and pipeline under development.
◆'SAFA Platform' with Extended Half-Life and Reduced Side Effects..."Expected to Remain in the Body for 20 to 25 Days"
AprilBio has been developing pipelines based on two core technologies: an antibody library and a long-acting platform.
First, the 'HuDVFab antibody library' of April Bio constructed two libraries by separating the heavy and light chains that make up the Fab after extraction of PBMCs (peripheral blood mononuclear cells) from less than 40 healthy individuals. In particular, AprilBio's phagemid vector and plasmid vector were used to increase the expression of outer surface proteins of the virus by more than 100 times compared to the general phage display.
AprilBio uses the antibody library to shorten the screening time for human antibodies and to find candidates for antibody therapeutics against various target substances.
Another key platform is SAFA technology. Fabs with binding specificity to serum albumin are selected from the antibody library, and they are made into a fusion protein form with a substance having a therapeutic effect. When these protein drugs are administered, they bind to serum albumin which interacts with the FcRn receptor involved in protein recycling to prevent degradation, thereby developing long-acting drugs with a extended half-life.
CEO Cha said, "Albumin accumulates in the tumor microenvironment(TME) and inflammatory sites". He explained, "Since drug-using SAFA technology accumulates more in the wound area than other long-acting drugs, there are advantages such as drug delivery, increased efficacy, and reduced side effects".
AprilBio predicts that the residence time of the drug applied with SAFA technology will be about 20 to 25 days in the human body. Therefore, in the clinical trial, they expect that it can be developed as a method of administering the drug once every 2 to 4 weeks. Especially, the drug-using SAFA technology is effective even with lower drug concentrations since it is efficiently delivered to the inflammatory area and has an extended half-life. CEO Cha said, “If the SAFA technology is applied, it will show sufficient efficacy with a dose of about 1/3 to 1/7 than before.”
He pointed out that other advantages of SAFA technology are easy quality control and high production efficiency. He mentioned that “Compared to the competitive technology such as Nanobody, SAFA uses a 50kDa-sized Fab to induce it to naturally bind to serum albumin, so the chemical bonding is not required and glycosylation does not occur, making quality control easy".
He also explained that it can be manufactured using one protein production system unlike other technologies since it is expressed in the form of a fusion protein. Therefore it is highly competitive in terms of production efficiency.

◆ Competitive Technology, Ablynx's 'Nanobody'
AprilBio chose the Nanobody technology of Ablynx in Belgium as a competitive technology. Nanobody is an antibody discovered in camelids and has a unique structure with only a heavy chain region that binds to an antigen and no light chain. Compared to general antibodies, it is 1/10th the size, so it is easy to administer and can be bound with up to 7 targets with one drug by combining several nanobodies.
Ablynx has collaborations with multiple pharmaceutical companies including Sanofi, Abbvie, Merck, and Novartis based on nanobody technology to conduct joint development. Meanwhile, Sanofi acquired Ablynx for about $4.8 billion (about 5.7 trillion won) in 2018. Afterward, 'Cablivi (caplasizumab)', a drug-using Nanobody technology, was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2019 following Europe in 2018. Cablivi is approved for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP) and is being sold in the US and Europe, with sales of about $134 million last year.
Most pipelines based on Nanobody use albumin-binder technology, similar to AprilBio's SAFA. Examples include the IL-17FxIL17A/F bi-specific antibody 'M1095', which is co-developing by Sanofi and MSD, and the TNF-α antibody 'ozoralizumab', which is jointly developing with Taisho. M1095 is undergoing a global phase 2 clinical trial, and ozoralizumab is undergoing a phase 3 clinical trial in Japan.
◆ Lead Pipeline CD40L Antibody 'APB-A1'… "Enters Phase 1 Clinical Trial This Year"
He said “Currently, we are focusing on the development of the CD40L antibody 'APB-A1'” and “The results of phase 1 clinical trials of APB-A1, the candidate of autoimmune disease therapeutics entering clinical trials this year, will be able to confirm next year”. He then emphasized, "If we go beyond the level of proof-of-concept (PoC) study in animal models and confirm the actual effectiveness of SAFA technology in clinical practice, technology transfers and partnerships will be more active."
AprilBio's APB-A1 is one of the TNF molecules and is expressed on activated T cells. CD40L regulates the proliferation and differentiation of B cells by binding to CD40 expressed in B cells. It can regulate the immune response by selectively inhibiting T cells through this interaction between CD40L/CD40.
The drug that was developed with this concept is Biogen's 'ruplizumab'. Ruplizumab, which was developed as a treatment for autoimmune diseases, had a serious adverse event called thromboembolism. So, its development was discontinued in phase 2 clinical trials.
This adverse event is known to be caused by the binding of CD40L Fc and the FcγRIIa on the platelet surface. AprilBio has developed 'APB-A1', which removes the Fc region of CD40L and binds SAFA to block CD40L/CD40 signaling, increase half-life, and suppress side effects.
In fact, as a result of administering APB-A1 at different concentrations to human PBMC cell lines, suppressing B cell differentiation was confirmed. In addition, when the positive control ruplizumab was administered, platelets were aggregated in a concentration-dependent manner, but it was confirmed that platelets did not aggregate when APB-A1 was administered.
Besides, the IL-18 antibody 'APB-R3' is being developed. IL-18 is a pro-inflammatory cytokine. It stimulates CD8 T cells and NK cells to promote the production and expression of INF-γ. Overexpression of IL-18 causes macrophage activation syndrome (MAS) and various autoimmune diseases.
AprilBio's APB-R3 is a drug that binds SAFA to IL-18BP (binding protein) and is being developed targeting inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and rheumatoid arthritis. APB-R3 binds to IL-18 and inhibits INF-γ, a type of inflammatory cytokine, to lower the immune response to treat inflammatory diseases.
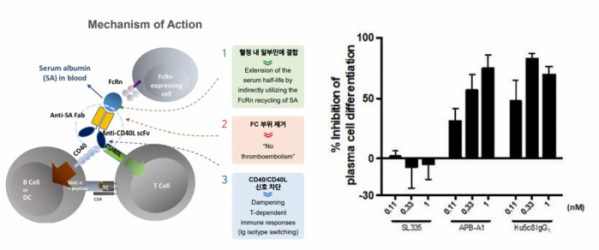
▲Left) MoA of APB-A1 ; Right) suppressing B cell differentiation

















