탐방
BaobabAI, New Drug Development based on ‘Cryo-EM+Quantum Mechanics and AI’
by Yoonseok Suh
Precise Analysis of ‘Undruggable’ Protein Structure based on Cryogenic Electron Microscopy (Cryo-EM) + Rapid Analysis of Large-Scale Data based on Quantum Mechanics and Artificial Intelligence..Aim to

In-sang Lee, CEO of Baobab AiBio, said “With cryogenic electron microscopy (Cryo-EM), we will analyze the protein structure that could not be done with the existing X-ray crystallography technology, and proceed with the efficient and rapid development of new drugs through quantum mechanics and artificial intelligence (AI) technology”.
Baobab AiBio was established in 2018 by Professor Kyoung Tai No of Yonsei University and Professor Tae-il Kim of Yonsei University. In 2019, president In-sang Lee joined as the new drug development manager from LG Life Sciences, and the company switched to the co-representative system of Kyoung Tai No and In-sang Lee. The company moved from Yonsei University in Sinchon to the Yonsei University International Campus in Songdo, Incheon in 2019. Baobab AiBio, founded at Yonsei University as the faculty startup, has been invested by GenoFocus since its establishment. Songamsa, the holding company of Shinpoong Pharmaceuticals, also invested about 3 billion won. In March, it succeeded in attracting 16 billion won with Series A.
CEO No has been operating the Bioinformatics and Molecular Design Research Center (BMDRC), an incorporated corporation, for about 25 years since 1997, and it is not an exaggeration to say that it has been with the history of the artificial intelligence (AI)-based new drugs in Korea. CEO Lee explained that most of the former researchers of the Bioinformatics and Molecular Design Research Center are working in domestic AI-based drug development companies.
Baobab AiBio's new drug development platform is Bio-Space Voyager. CEO Lee said, “It means to navigate the vast bio space to discover drugs. Our platform makes it possible to discover and develop differentiated new drugs based on accurate protein structure analysis through Cryo-EM, reliable drug design through artificial intelligence (AI), and rapid large-capacity computing power through quantum mechanics.
Particularly, the Cryo-EM is the equipment Baobab is proud of, which analyzes the structure of proteins with atomic-level resolution. Baobab is the first private enterprise to invest about 8 billion won to build Cryo-EM. The primary goal is to fully establish the Cryo-EM equipment within this year. At the same time, it plans to complete the phase I clinical trial for familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) within the second quarter of this year. Biospectator looked into Baobab AiBio's new drug discovery platform technology using Cryo-EM.

◆ New drug discovery based on cryogenic electron microscopy (Cryo-EM)..”Structural analysis of undruggable proteins”
① What is cryogenic electron microscopy (Cryo-EM)?
CEO Lee said “Cryo-EM is essential equipment for new drug development, and there are fewer than 10 devices government-funded research institutes and universities in Korea. ” He emphasized “We purchased it for the intensive use of Cryo-EM in the development of new drugs" Baobab pointed out the implementation of Cryo-EM by the first quarter of next year as the most important short-term milestone. Cryo-EM analyzes the three-dimensional structure at the atomic level by rapidly freezing samples such as proteins at an ultra-low temperature of -196 degrees and taking images from multiple angles while maintaining the original state of the material.
There are three types of Cryo-EM that Baobab builds: Glacios (Cryo-EM/Micro ED Glacios (200KV)) Krios (Cryo-EM/Cryo-ET Krios(300KV))and from Thermofisher Scientific, and Aquilos (Aquilos2, focused ion beam) for preparing samples of Cryo-EM.
In addition to the single-particle analysis (SPA) function, Glacios has an electron diffraction device, Micro-ED, and Krios has an electron tomography device, Cryo-ET, respectively.
First, SPA is a technology that can analyze the structure of a single substance and it was used to analyze the structure of the virus for the development of a vaccine in the current COVID-19 situation. Next, Micro-ED included in Glacios measures the diffraction of electrons to analyze the structure of the protein, and it is possible to experiment even at the level of 1/100 of the protein sample used in conventional X-ray crystallography. X-ray crystallography uses x-rays to measure the diffraction of a crystal to analyze its structure. Finally, Cryo-ET included in Krios can take high-resolution images of protein aggregation, etc., which are necessary for research on Alzheimer's disease.
CEO No mentioned “In Korea, the only SPA is mainly used, and micro-ED and electron tomography are not set in Korea, so we plan to set it. Electron tomography can obtain high-resolution images enough to analyze the structure of proteins occurring in the body".
Cryo-EM has the advantages of △using a small amount of sample, △finding the structure of undruggable membrane proteins and large protein complexes, which were previously difficult to analyze, and △quickly obtaining results. CEO Lee said "When discovering new drug candidates, it is expected that the development period to the lead pipeline will be shortened by about 60%.”
Joachim Frank and Richard Henderson, who have been developing and researching early Cryo-EM since the 1970s, were awarded the 2017 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. It means that they were appreciated for their contribution to developing a technology that can analyze and image proteins at high resolution.
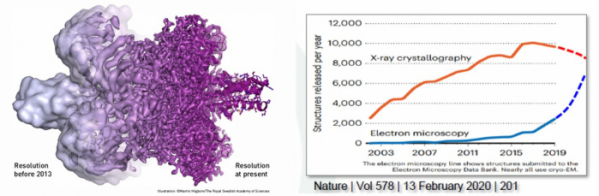
Currently, the resolution of Cryo-EM has been increasing with the advancement of technology. The current resolution of Cryo-EM has improved beyond the level of 3.6Å, which is the level of X-ray crystallography, to 2Å or more. The 2Å resolution is a level that can observe proteins down to the atomic level (doi:10.1038/d41586-020-02924-y). For this reason, the use of Cryo-EM to elucidate the structure of proteins is increasing. This can be confirmed by the picture of the resolution development process from 2013, which was announced at the time of the Nobel Prize for Cryo-EM, and by the structural analysis using Cryo-EM, which rapidly increased from hundreds to thousands of cases around 2015. (doi:10.1038/d41586-020-00341-9).
② What are the Cryo-EM use cases?
CEO Lee said “As a representative example, Pfizer was able to develop a vaccine quickly during the COVID-19 pandemic because of the rapid and accurate analysis of the virus structure with Cryo-EM”. Practically, in February 2020, the structure of the spike protein of the Corona 19 virus was revealed by Cryo-EM, just three months after the first COVID-19 patient was identified in Wuhan, China in November 2019(doi: 10.1126/science.abb2507). Based on the analyzed structure of the COVID-19 virus, Pfizer and Moderna were able to quickly develop a vaccine.
Another example is that new drugs can be developed by analyzing the structures of targets that were previously difficult to develop as drugs. For instance, kinase-targeted drugs were undruggable targets before their structures were discovered, but structures began to be elucidated through X-ray crystallography in 1991. Since 1997, when structural data have been accumulated, kinase-based drugs get down entering clinical trials. CEO Lee said “The structure of GPCRs has been analyzed through Cryo-EM since 2017, and many GPCR-based drugs are expected to start clinical trials in the near future”.
③ Accelerate discovery of new drugs by helping with large-scale data analysis
Cryo-EM takes pictures for about 3 days of quick-frozen samples, and when one sample is taken, about 1800 images are produced. Since 3D images are created by taking pictures in various directions, large amounts of high-resolution data are generated, and it takes about 4 days just to analyze them.
Baobab is upgrading synthetic drug and protein drug artificial intelligence (AI) discovery platform, quantum mechanics algorithm, quantum computing and artificial intelligence technologies that quickly analyze large amounts of data. Specifically, it is explained that it is possible to obtain highly reliable data by analyzing the tertiary structure data of the protein obtained from Cryo-EM based on quantum mechanics algorithm (fragment molecular orbital, FMO) and increasing the target-ligand structure prediction to 99% using artificial intelligence technology. Quantum computing technology is also being developed.
◆ Targeting the Hippo Pathway for New Anti-cancer Therapies.."Aim to Apply for Phase 1 IND Next Year”
CEO Lee said “We plan to complete phase I clinical trial for familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) with ‘BAB-101’, a leading pipeline Axin-GSK3 inhibitor, by the second quarter of this year”. FAP is a rare disease that occurs in about 1 in 10,000 people, and there is currently no approved treatment for it. Existing Cox inhibitors showed efficacy in phase III clinical trials, but approval was withheld due to safety issues.
Next, Baobab is conducting research on 'BAB-104', which inhibits YAP, an oncogene related to the HIPPO pathway, and TEAD, a transcription factor, for glioblastoma, lung cancer, and blood cancer. It plans to secure candidate substances by this year and apply for a phase 1 clinical trial plan (IND) within next year.
As a competitor, Vivace Therapeutics started the phase 1 clinical trial of 'VT3989', a YAP-TEAD inhibitor, targeting methoselioma and glioblastoma this year.



















